Special sondes
Overview
Special sondes (radiosondes with special sensors not present in regular GPS sondes) are used to monitor meteorological variables such as water vapor and ozone concentration that are not covered by routine aerological observation, and for high-accuracy temperature and humidity monitoring to produce research data.
The Aerological Observatory currently operates a temperature reference sonde (MTR) and a water vapor reference sonde (SKYDEW), and has previously operated units for water vapor (CFH), radioactivity, longwave radiometry, atmospheric electricity and dewpoint.
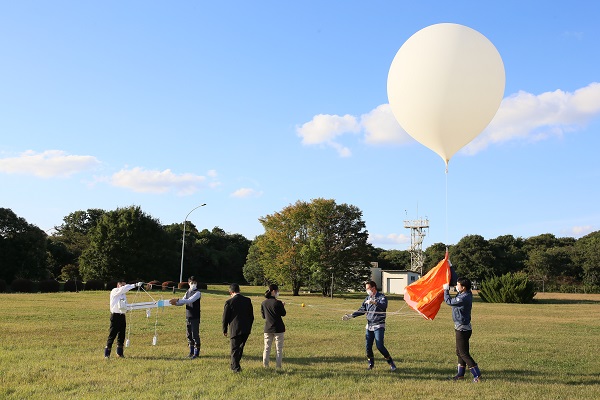

Special sonde launch
Temperature reference sonde (MTR)
An MTR is a specialized radiosonde used to monitor temperature with higher resolution than a routine GPS sonde. The aluminum coating on its temperature sensor reduces the influence of solar radiation, and the unit monitors temperature 16 times per second with a sensitivity of 0.01℃. MTR flights are conducted twice a year.
Data from the unit are referenced in international comparison and research toward improved temperature observation using GPS sondes.
| Metric | Monitoring technology |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Aluminum-coated tungsten sensor |
| Pressure | Connected GPS sonde |
| Data | GPS sonde transmission |

Temperature reference sonde (MTR) (transmitter: RS-11G)

Temperature reference sonde (MTR) launch
Water vapor reference sonde (SKYDEW)
A SKYDEW sonde monitors atmospheric water vapor with high accuracy. Dewpoint/frost point temperature is calculated from the temperature at which dew/frost forms on the cooled mirror surface within the unit. The use of a Peltier device for cooling eliminates the need for refrigerant and reduces the unit’s environmental impact. Atmospheric water vapor concentration is also calculated from temperature/pressure measured using the unit’s GPS sonde. SKYDEW flights are conducted twice a year.
Data from the unit are referenced in international comparison and research toward improved humidity observation using GPS sondes.
| Metric | Monitoring technology |
|---|---|
| Dewpoint/frost point temperature | Reference to the temperature at which dew/frost forms on a cooled mirror surface. |
| Temperature/pressure | Connected GPS sonde |
| Data | GPS sonde transmission |

Water vapor reference sonde (SKYDEW) (transmitter: RS-11G)

Water vapor reference sonde (SKYDEW) launch
Previous special sondes
Water vapor reference sonde (CFH) (2015 - 2021)
A water vapor reference sonde (CFH; a hygrometer developed at the University of Colorado) measures dewpoint/frost point based on the temperature at which dew/frost forms on its CHF3-cooled mirror surface. It measures atmospheric water vapor concentration with high accuracy from the surface to the stratosphere.
Water vapor reference sonde (CFH)
Radioactivity sonde (1959 - 2006)
A radioactivity sonde measures atmospheric radioactivity intensity. It was initially developed to monitor artificial radioactivity associated with hydrogen bomb experiments.

Radioactivity sonde (RC-94)
Longwave radiometer sonde (1965 - 1977)
Longwave radiometer sondes observe atmospheric infrared radiation, which is a major factor in atmospheric circulation and atmospheric physics.

Longwave radiometer sonde (R69)
Atmospheric electricity sonde (1957 - 1977)
Atmospheric electric sondes measure atmospheric electrical conductivity and current intensity associated with the large potential difference between the Earth's surface and the ionosphere, which is also associated with lightning.

Atmospheric electricity sonde (E70)
Dewpoint sonde (1957 - 1977)
Dewpoint sondes measure dewpoint temperature and observe trace amounts of stratospheric water vapor, which greatly affects photochemical reactions in the ozone layer and other areas.
Dewpoint sonde (H70)