Aerological Observation (GPS sonde Sounding)
Aerological observation
The Aerological Observation Division launches GPS sondes (instruments for collecting meteorological data) suspended from balloons and observes profiles of pressure, temperature, humidity and wind twice a day.
There are around 800 upper-air sounding sites worldwide. At each one, GPS sondes are launched simultaneously at 00 and 12 UTC (09 JST and 21 JST). In Japan, extra GPS sondes are occasionally launched for observation of tropical cyclones, experiments and other work.

GPS sonde launch
GPS sonde
GPS sonde consists of a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, a GPS antenna, processors and electric circuits.
| Metric | Measurement method(iMS-100) | Measurement method(RS41-SG) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Thermistor | Platinum Resistor |
| Humidity | Electrostatic capacity type | Thin-film capacitor |
| Wind direction | GPS wind finding | GPS wind finding |
| Wind speed | GPS wind finding | GPS wind finding |
| Altitude | Calculated from GPS | Calculated from GPS |
| Pressure | Calculated from GPS | Calculated from GPS |

iMS-100 GPS sonde

RS41-SG GPS sonde
Examples
Example profiles are shown below. The vertical axis represents altitude or pressure, and the horizontal axis represents a metric (temperature, humidity, wind direction or wind speed). These figures depict upper-atmospheric conditions.
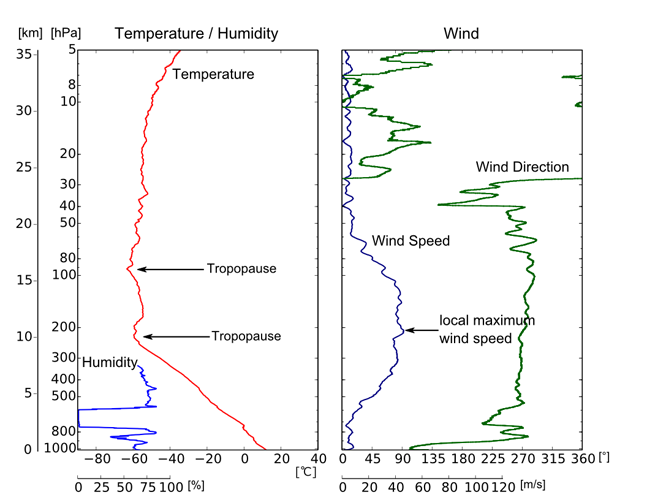
Upper-air profiles. Left: temperature (red) and humidity (blue). Right: wind direction (green) and wind speed (blue).