DCS and DCPs
Introduction
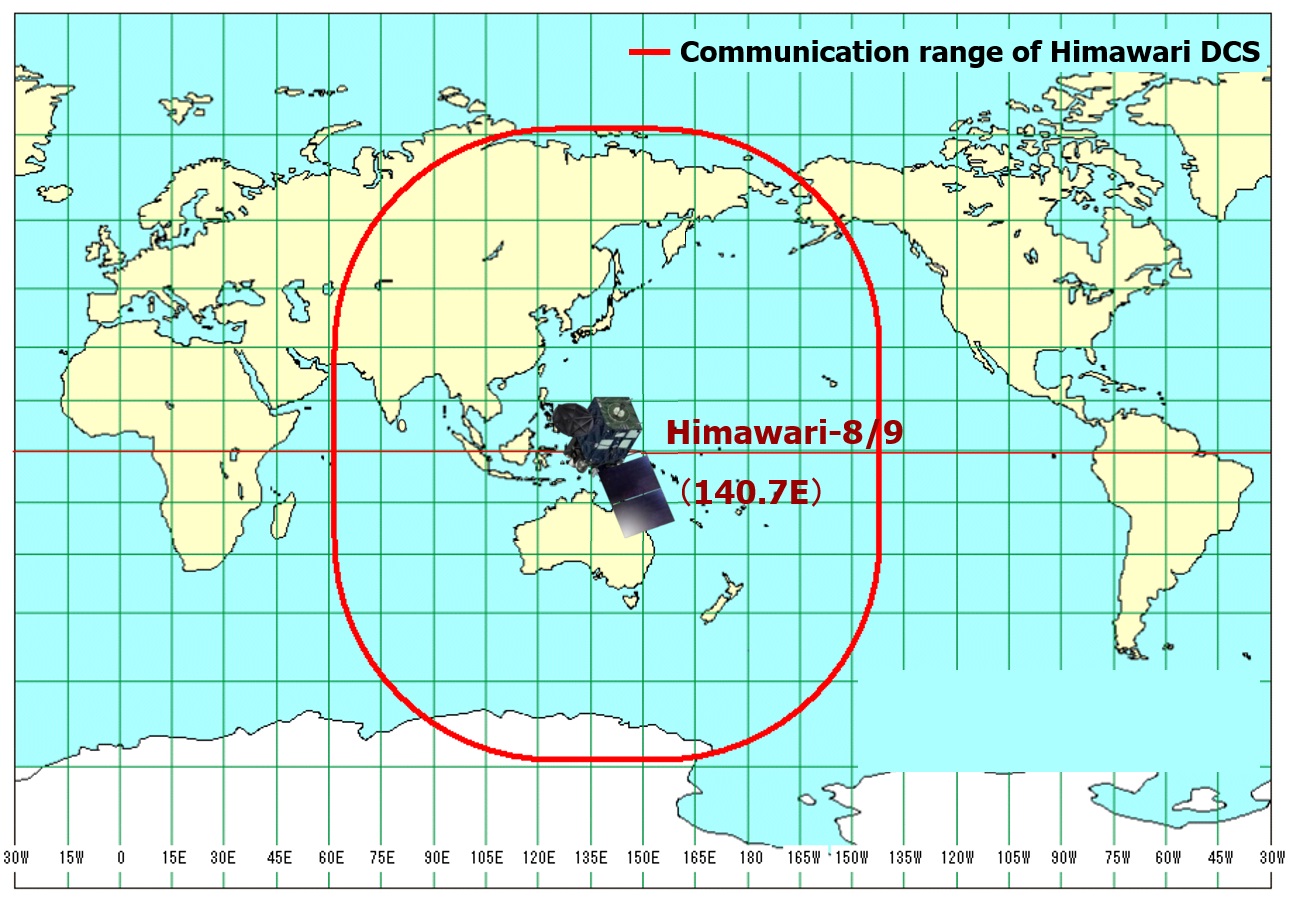
The Data Collection System (DCS) is used to collect and relay data via earth-based observation stations (Data Collection Platforms, or DCPs) within the communication range of geostationary satellites such as Himawari-8/9.
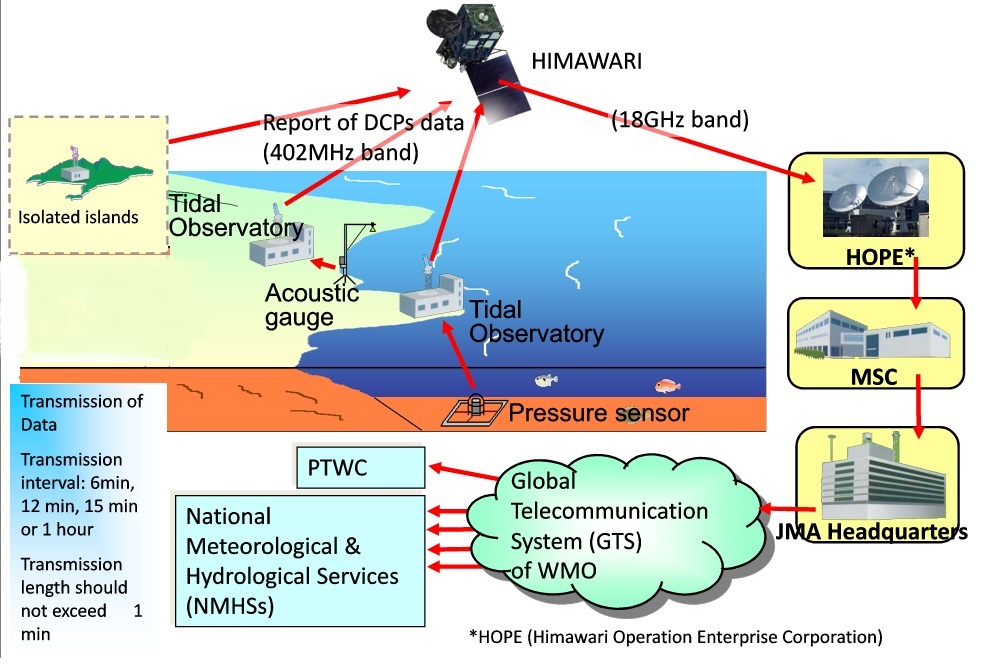
A DCP is an electronic device used to transmit observation data on atmospheric and oceanographic parameters such as temperature, pressure and tide levels. DCPs within Himawari-8/9’s communication range encode and transmit observational data to the satellite, which in turn relays the information to ground stations operated by the Himawari Operation Enterprise (HOPE). HOPE then sends the data to JMA for processing and provision of related products to users, and the data are finally provided to DCP operators and users via the Global Telecommunication System (GTS).
In addition to the DCP support function, the Himawari-8/9 DCS supports exchanges of earthquake-related information. The satellite collects seismic intensity data from earthquake observation sites all over Japan. Its DCS also supports dissemination of emergency tsunami/earthquake information within the Himawari-8/9 communication range.
IDCS and RDCS
Himawari-8/9 supports the International DCS (IDCS) and Regional DCS (RDCS) data collection systems. IDCS is designed to support DCPs stationed on moving vehicles that moving between the communication coverage of Himawari-8/9 and other satellite. RDCS is designed to support fixed DCPs such as automated remote weather stations and tide/tsunami gauges within the Himawari-8/9 communication range.