Calibration for atmospheric greenhouse gases and reactive gas observation
Scale for atmospheric gas observation
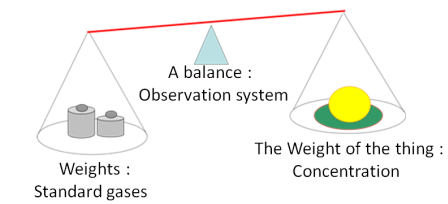
To determine the exact concentrations of small amounts of greenhouse gas species in the atmosphere, samples are compared with corresponding standard gases whose concentrations are already known (Figure 1) .
In order to enable the comparison of concentration data collected at JMA observation stations with others from around the world, an international standard scale is required for all standard gases used worldwide (in terms of surface ozone monitoring) that form the basis of gas observations. JMA performs calibration to keep its standard gases (for ozone monitoring) consistent with the global standard.
|
Figure 1: Concept of observation using standard gases |
Calibration
To enable comparison of observation data characterized by temporal and spatial differences, the measurement scales used need to be standardized. Against such a background, calibration is necessary to ensure the traceability (by which the relationships linking scales used for individual observations are set) of observations. In calibration, the observation scale is compared with a certain standard and adjusted as necessary before observation is carried out.
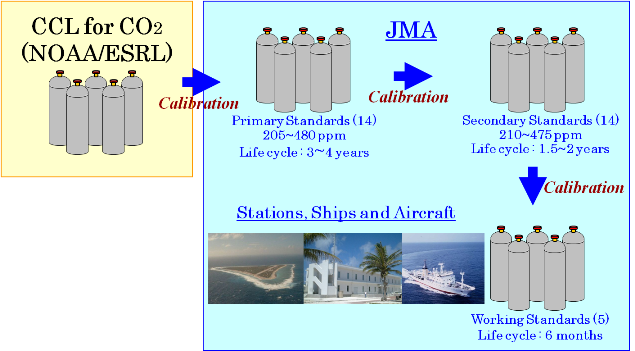
Calibration work is essential for accurate determination of environmental changes based on global observation. JMA performs calibration to link its standard gases (for monitoring of surface ozone) to WMO's global standard scales (Figure 2) .
|
Figure 2: JMA calibration architecture (CO2) |
Related contents
- Calibration method of gas species ( Carbon dioxide Methane Nitrous oxide Carbon monoxide Surface ozone )