Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are compounds of carbon, fluorine and chlorine, are artificial substances with greenhouse effects and ozone-depleting potential.
Related emissions are regulated under the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer and its Amendments and Adjustments.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are compounds of carbon, hydrogen and fluorine, are CFC alternatives that do not deplete stratospheric ozone but have significant greenhouse effects, and are also regulated.
The figure below showing CFC-11, CFC-12 and CFC-113 mole fractions over time at JMA's Ryori Station (observation ended in March 2024) exhibits slight short-term variations with no seasonal variability. Values for CFC-11 peaked at about 270 ppt in 1993 - 1994, and have since decreased. Those for CFC-12 increased until 1995 and rose gradually thereafter, peaking in 2005. Those for CFC-113 show little change in the 1990s and a slight decrease in recent years.
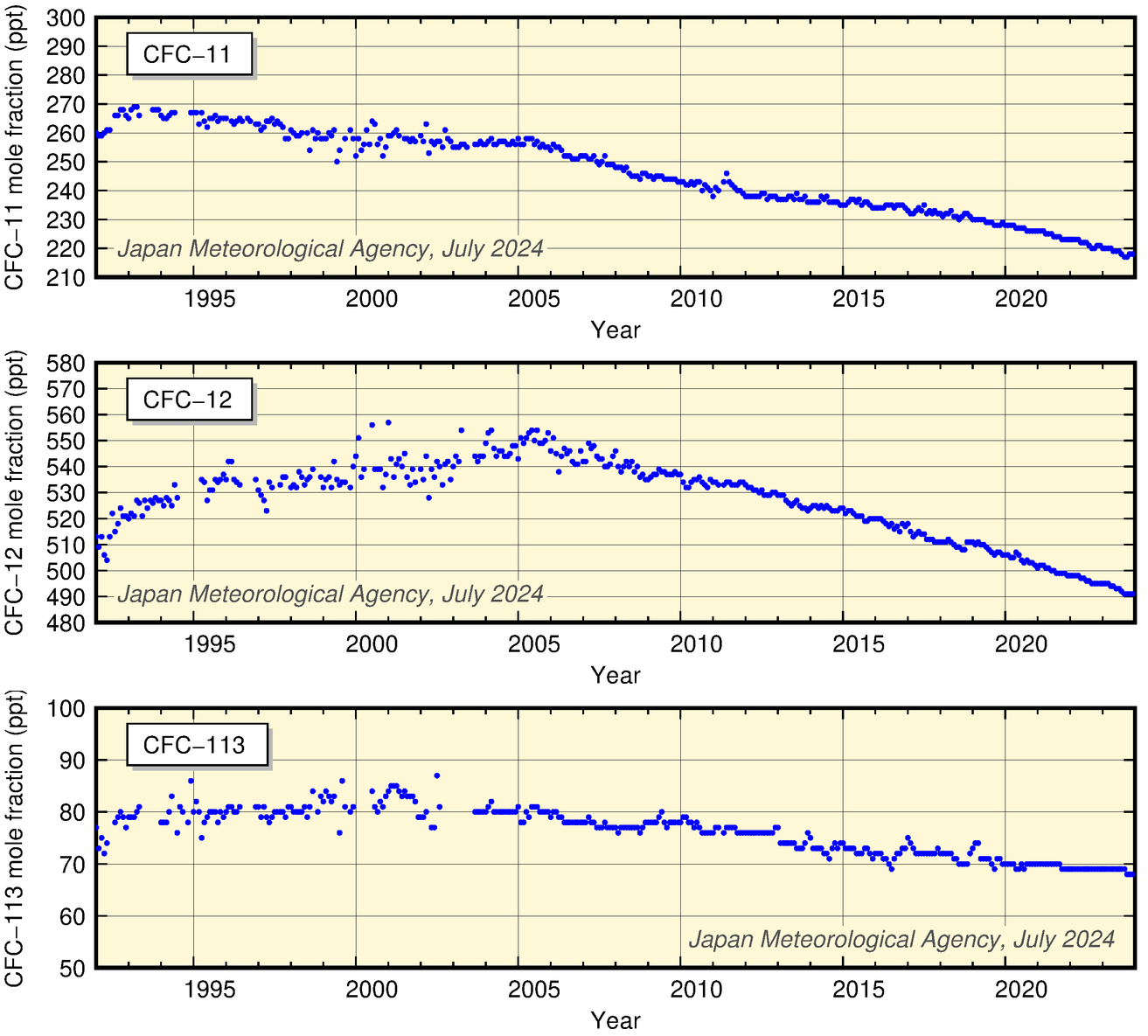
Monthly mean atmospheric conentrations of CFC-11 (top), CFC-12 (middle) and CFC-113 (bottom) at JMA observatory
Provisional values are included. Observation at Ryori ended in March 2024.
The figure below shows HFC (HFC-23, HFC-32, HFC-125, HFC-143a, HFC-134a, HFC-152a, HFC-227ea, and HFC-245fa) mole fractions over time at JMA's Minamitorishima Station.
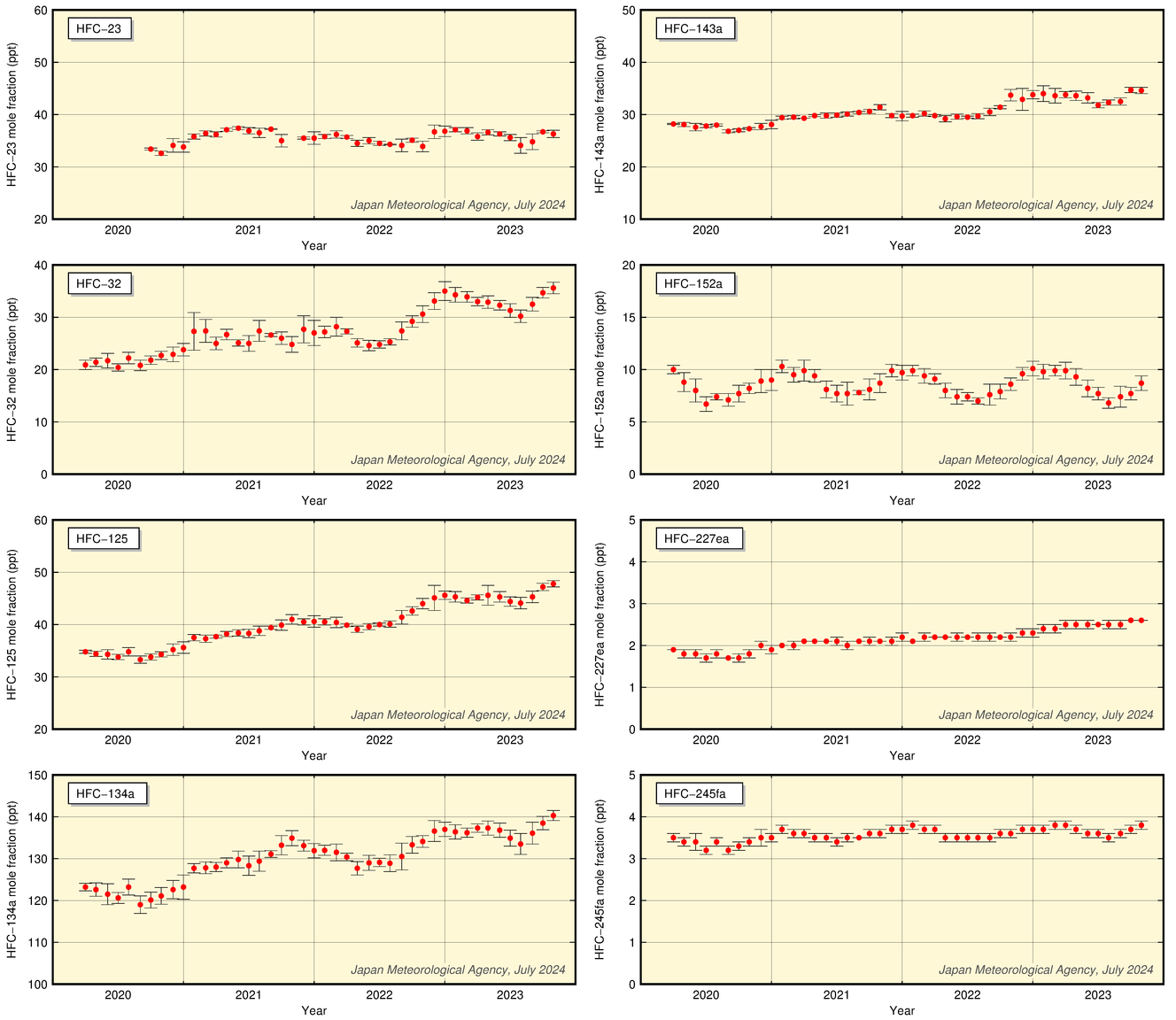
Monthly mean atmospheric concentrations of HFCs at JMA's Minamitorishima observatory
Values are provisional.
· Some HFC-23 data are missing due to equipment problems experienced between April 2020 and September 2020.
Worldwide WDCGG observation data show increased CFC mole fractions associated with industrial production followed by the start of a decrease due to industrial regulation based on the Montreal Protocol.
CFC-11 mole fractions peaked around 1992 before starting to decrease, those of CFC-12 increased until around 2003 before starting a gradual decrease, and those of CFC-113 stopped increasing in the 1990s before starting a slight trend of decrease over the subsequent period of around 20 years.
Values for CCl4 peaked around 1991 and have since shown a gradual decrease. Those for CH3CCl3 peaked around 1992 and have since decreased.
Halon-1211 mole fractions have decreased since 2005, and growth in Halon-1301 values has levelled off in recent years.
Mole fractions of HCFCs (HCFC-22, HCFC-141b, HCFC-142b), used mainly as substitutes for CFCs, have increased significantly during the last two decades but have levelled off in recent years.
Values for HFC-134a and SF6 show an increase, while those for HFC-152a have levelled off in recent years. Values for CH3Cl show no significant long-term tendency, although a clear seasonal cycle is seen in the dataset.
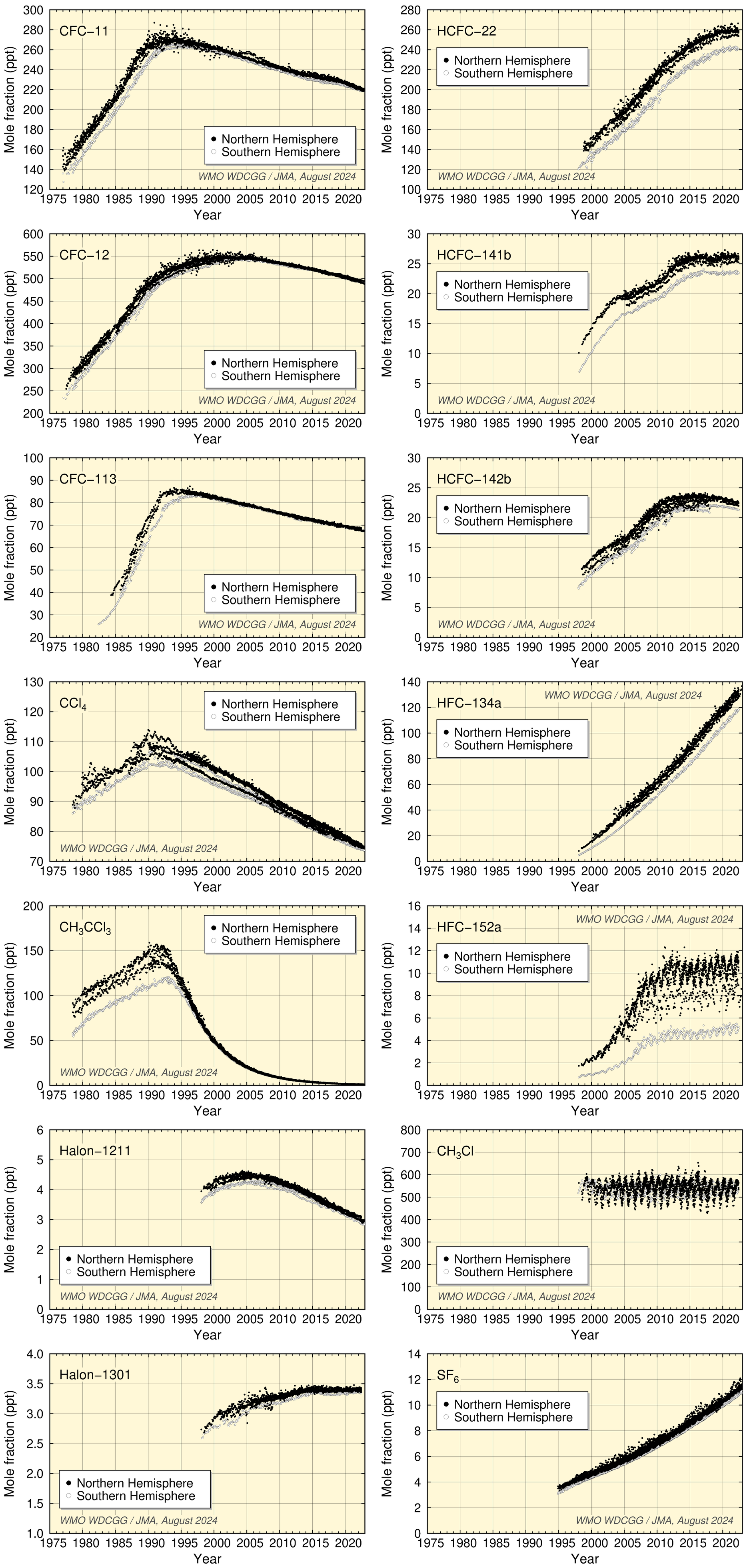
Monthly mean concentrations of halogenated-species as derived from worldwide observatories data